Business Owner Responsiveness to Employee Ownership Outreach Efforts
Author:
Vipul Bokil
Doctoral Candidate
Katz Graduate School of Business University of Pittsburgh
Questions: What characteristics of businesses and business owners impact their responsiveness to employee ownership as a business model? Do different outreach messages influence their responsiveness differently, and if yes, how? Generally, what conditions make business owners more receptive to information about employee ownership?
Summary: Analyzing quantitative and qualitative data collected as part of a Pittsburgh citywide employee ownership awareness initiative, we find that the type of messaging used by outreach campaigns influences responsiveness among target business owners. Moreover, this influence varies by business and business owner characteristics including firm size, industry, and the business owner’s gender. This research finds that not all outreach methods yield the same level of response to messaging.
Emphasis on certain aspects of employee ownership and focused messaging are important for the success of outreach campaigns. The choice of communication channel, frequency of messaging, and fitment of message with recipients influence the effectiveness of a campaign. Not all businesses or business owners are the same, and messaging should be sensitive to these differences.
The Pittsburgh Citywide Taskforce on EO
- This research evaluates outreach methods to promote EO as a succession option among Pittsburgh-area business owners, particularly those considering exit strategies.
- The outreach, initiated by the Pittsburgh City Council and the Pennsylvania Center for Employee Ownership, aimed to increase EO awareness among business owners by using an informational website and community workshops.
- Outreach included physical mail (33,314 businesses) and email (3,789 business owners), with recipient details sourced from public business directories and professional networking platforms like LinkedIn and Yelp.
- Businesses were randomly assigned one of the two message types:
- Social message: emphasis on benefits to workers and the community.
- Financial message: emphasis on financial benefits to the business owner.
- 3 emails and 2 physical mails (a letter and follow-up card) were sent. Unique URLs embedded in communications allowed monitoring of individual website visits, workshop enrollments, and inquiries, producing the data we analyzed.
Message Type and Communication Platform
- Aggregate response rates varied substantially by communication platform. Email outreach received a 2.37% response rate while physical letter outreach received 0.31% (Fig. 1).
- Disaggregation by message type finds that social messaging receives a higher response rate than financial messaging in both email and letter outreach. This difference is more pronounced in email outreach.

Firm Performance and Message Type
- Response rates were examined by two indicators of businesses’ financial position: sales per employee and credit rating. When aggregated, there is no noticeable difference, but disaggregating by message type makes differences evident.
- Businesses responding to social messaging had median revenue per employee that was about 16% higher than non-responding businesses (Fig. 2a).
- A similar pattern emerges for response rates by credit rating and message types. (Fig. 2b). Businesses doing better financially respond more positively to the message highlighting social benefits of employee ownership.


Firm Size and Message Type
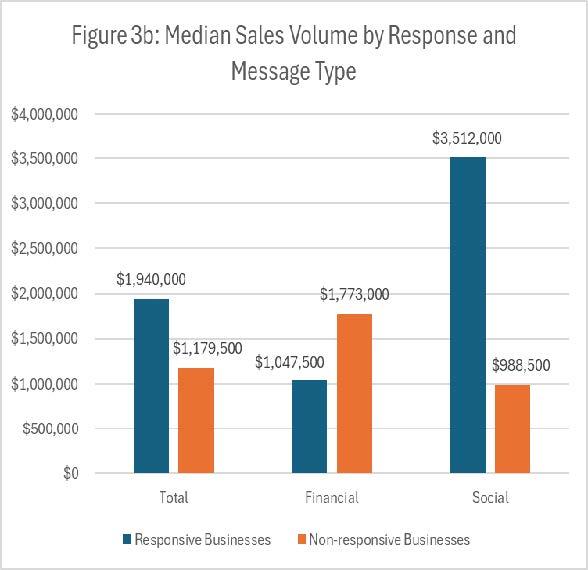
- Minimal difference is seen in response rates by the size of responding vs. non-responding businesses, but disaggregating by message type shows an interesting pattern.
- Among businesses receiving a financial message, smaller businesses respond better than larger ones. On the other hand, larger businesses respond better to a social message than smaller businesses. Figures 3a and 3b show these patterns for size determined by median revenue volume and median employee count.

Industry
- Business responsiveness varies by industry. Figure 4 lists response rates by 9 broad sectors.
- Food-related businesses (food manufacturing, retailing, eateries) are some of the most responsive industries. Table 1 lists 12 SIC-2 business categories with highest response rates.

Table 1: SIC-2 Business Categories with Highest Response Rate
| Sector | SIC-2 and Description | Response Rate |
| Retail Trade | 54 - FOOD STORES | 1.30% |
| Manufacturing | 20 - FOOD AND KINDRED PRODUCTS | 1.02% |
| Services | 89 - SERVICES, NOT ELSEWHERE CLASSIFIED | 0.93% |
| Wholesale Trade | 51 - WHOLESALE TRADE - NONDURABLE GOODS | 0.87% |
| Services | 72 - PERSONAL SERVICES | 0.78% |
| Retail Trade | 55 - AUTOMOTIVE DEALERS AND GASOLINE SERVICE STATIONS | 0.71% |
| Finance, Insurance and Real Estate | 64 - INSURANCE AGENTS, BROKERS AND SERVICE | 0.54% |
| Finance, Insurance and Real Estate | 65 - REAL ESTATE | 0.53% |
| Retail Trade | 57 - HOME FURNITURE, FURNISHINGS AND EQUIPMENT STORES | 0.51% |
| Manufacturing | 27 - PRINTING, PUBLISHING AND ALLIED INDUSTRIES | 0.49% |
| Retail Trade | 58 - EATING AND DRINKING PLACES | 0.43% |
| Construction | 17 - CONSTRUCTION - SPECIAL TRADE CONTRACTORS | 0.43% |
Message Recipient Gender and Message Type
- Response rates differ by recipient gender and message type.
- Male recipients have a higher overall response rate to physical letter outreach while female recipients show high overall responsiveness to email outreach.
- As Figures 5a and 5b show, on both communication platforms, female respondents tend to respond more positively to the social message than the financial message. The male response rate does not differ significantly between social and financial messaging on either platform.


Insights from Business Owner Interviews
We conducted semi-structured interviews with select owners of small, family-owned businesses who engaged with the outreach and attended workshops. These conversations revealed a balanced view of their key motivations, concerns, and patterns of outreach responsiveness.
Motivations for Considering EO
- Ensuring business continuity and fairness to workers in succession planning.
- Addressing employee engagement and accountability challenges.
- Strategic advantages in attracting and retaining talent through equity and voice.
- Personal and legacy-driven reasons, such as family history of employee welfare policies.
- Perceived financial benefits, tax advantages, and operational resilience.
- While financial considerations were noted, business continuity and legacy were more central motivators.
Concerns About Adopting EO
- Leadership readiness: Owners doubted employees’ ability to make important decisions.
- Organizational fit: Skepticism about EO in informal or non-business-oriented cultures.
- Complexity: Concerns about legal, operational, and structural hurdles to EO adoption.
- Some preferred conventional succession options due to perceived burdens of implementation.
Outreach Responsiveness
- Owners most responsive to outreach were actively exploring succession options. They sought information on EO beyond initial messaging and discovered additional benefits.
- Owners tended to focus on either social or financial benefits as central motivators, underscoring the importance of targeted messaging in outreach campaigns.
Conclusions
- Research Integration: Embedding intentionally designed research components into large outreach efforts offers opportunities to identify best practices while raising EO awareness.
- Follow-Up Matters: Response rates are notably higher after follow-up messages, highlighting the importance of sustained communication.
- Digital Preference: Email outreach yields higher response rates than physical letters.
- Industry Focus: Labor-intensive and food-related industries shows greater responsiveness, suggesting targeted outreach can improve results.
- Impact of Message Resonance: Social messages receives better engagement, particularly among larger, profitable businesses and female respondents. This underscores the value of tailored messaging.
- Insights from the Interviews:
- Owners consider both social and financial EO benefits but often prioritized one, stressing the need for focused messaging.
- Concerns include lack of information, legal/operational challenges, and owner’s skepticism about employees’ readiness to effectively implement EO.
- Owners actively seeking succession or exit options are more responsive, suggesting outreach should target these groups for greater impact.
Business Owner Responsiveness to Employee Ownership Outreach Efforts
Available at: https://www.aspeninstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Business-Owner-Responsiveness-to-Employee-Ownership-Outreach-Efforts-1.pdf